
Integratore alimentare a base di estratti vegetali in particolare con Tarassaco, Cardo mariano, Carciofo, Crisantello e Desmodium combinati per favorire le fisiologiche funzioni del fegato.

Plus di EPAVIN

Il Processo Spagyrico Brevettato potenzia
l’efficacia dei fitoestratti tramite:
separazione – potenziamento – riunione
degli attivi delle piante.
Il 35% della popolazione adulta ha una forma di steatosi epatica non alcolica (NAFLD).
La Non Alcholic Fatty Liver Disease è una manifestazione epatica delle patologie metaboliche e comprende diversi stadi di patologie epatiche che vanno dalla steatosi alla cirrosi epatica.
FITOESTRATTI DI ORIGINE SPAGYRICA
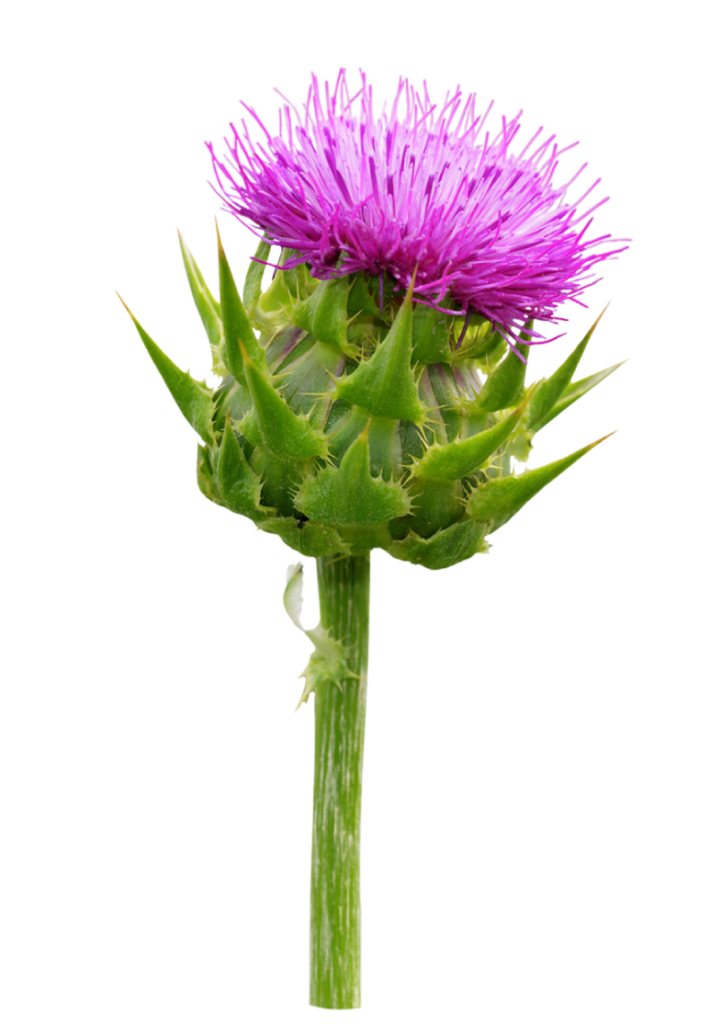

Cardomariano
Stimola la sintesi proteica negli epatociti e coadiuva la loro rigenerazione.
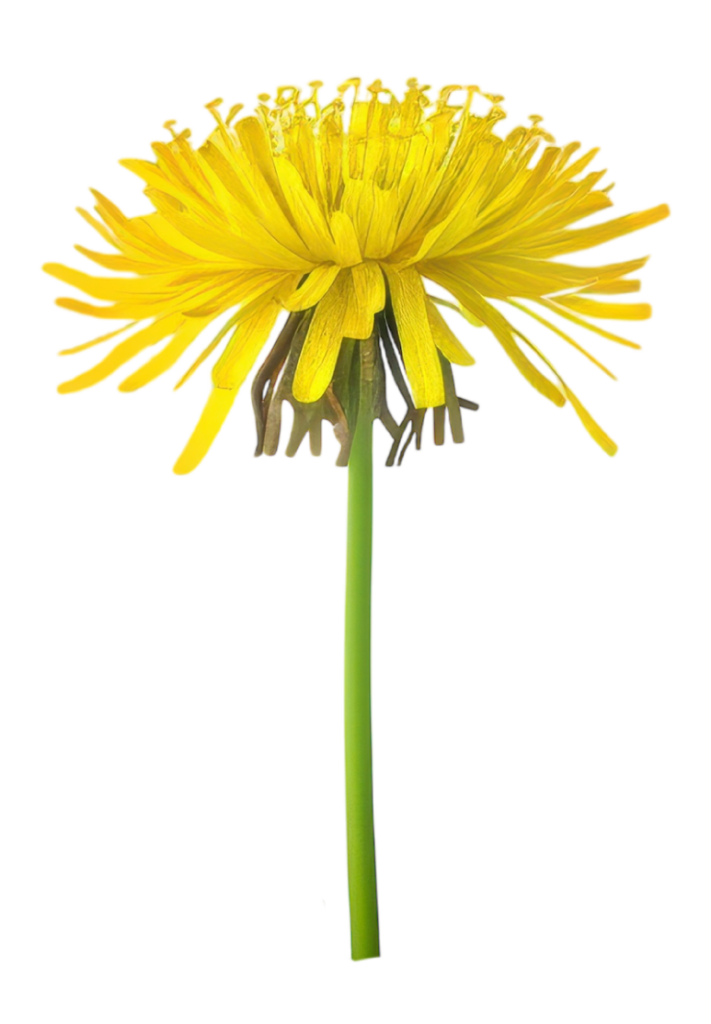

Tarassaco
Depura dalle tossine idrosolubili e svolge azione coleretica sulla bile.
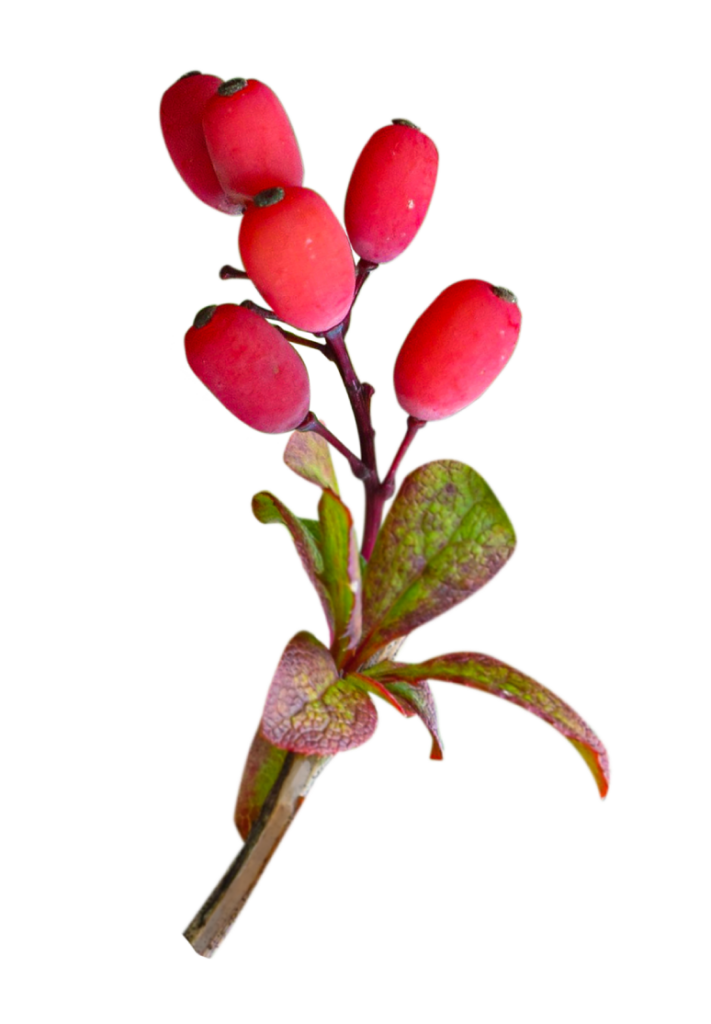

Crespino/Berberina:
Capta il glucosio cellulare riducendo la glicemia e mantiene l’omeostasi del glucosio epatico.
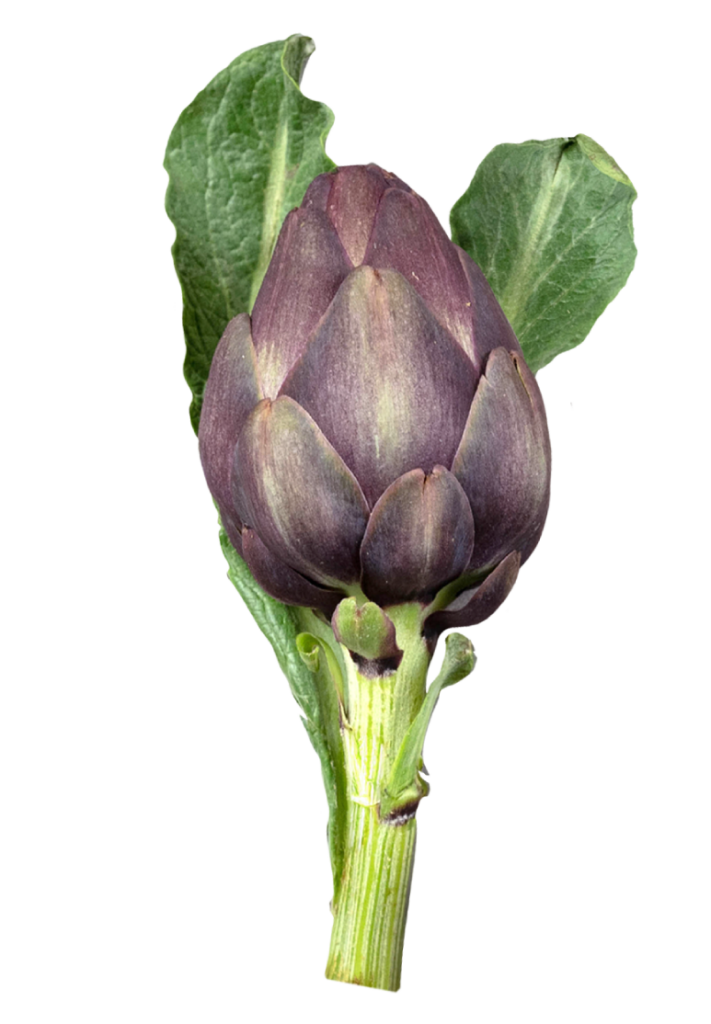

Carciofo
Ha azione colagoga sulla bile, diminuisce il colesterolo endogeno agendo a livello recettoriale.
10 FITOESTRATTI
DA TINTURE MADRI SPAGYRICHE
CHE:
Sostengono la funzionalità epatica
Coadiuvano nelle terapie metaboliche
Sostengono i differenti meccanismi digestivi
Hanno azione chelante sui metalli pesanti


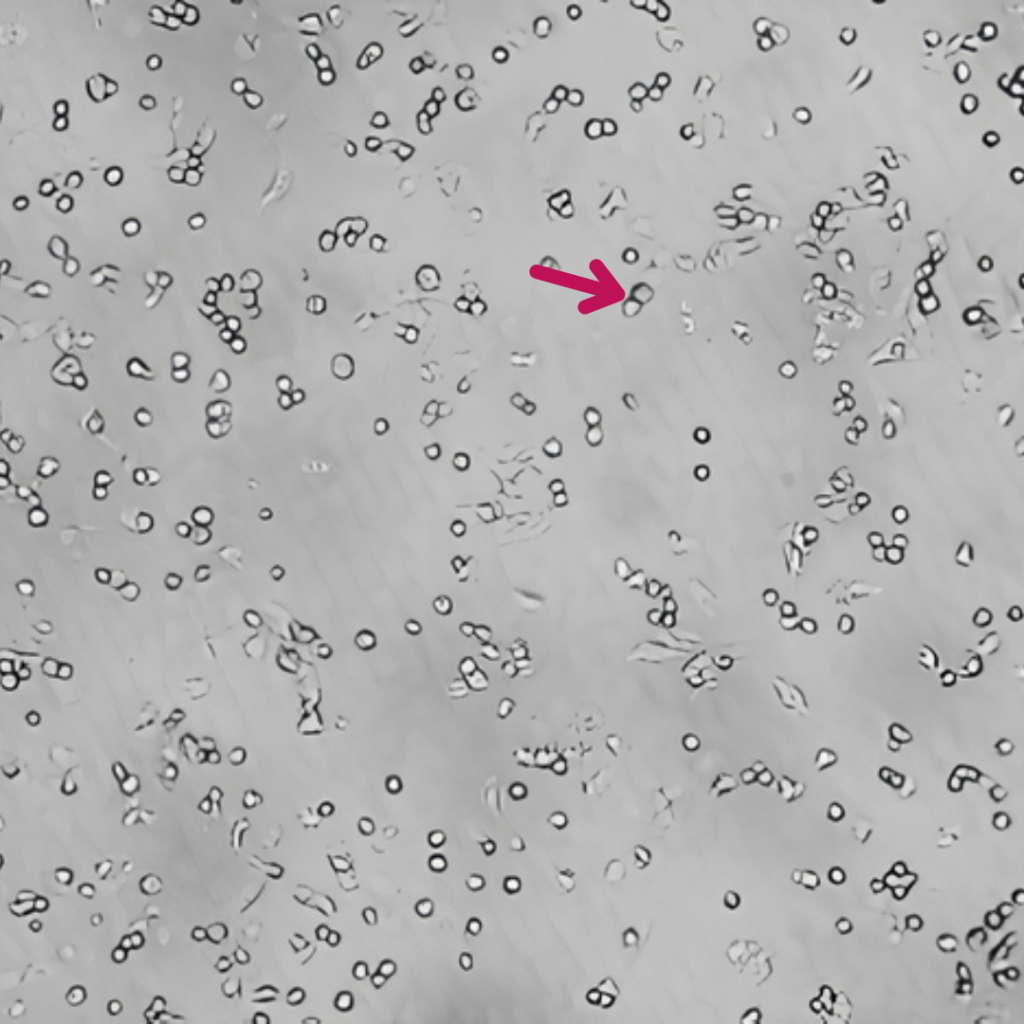
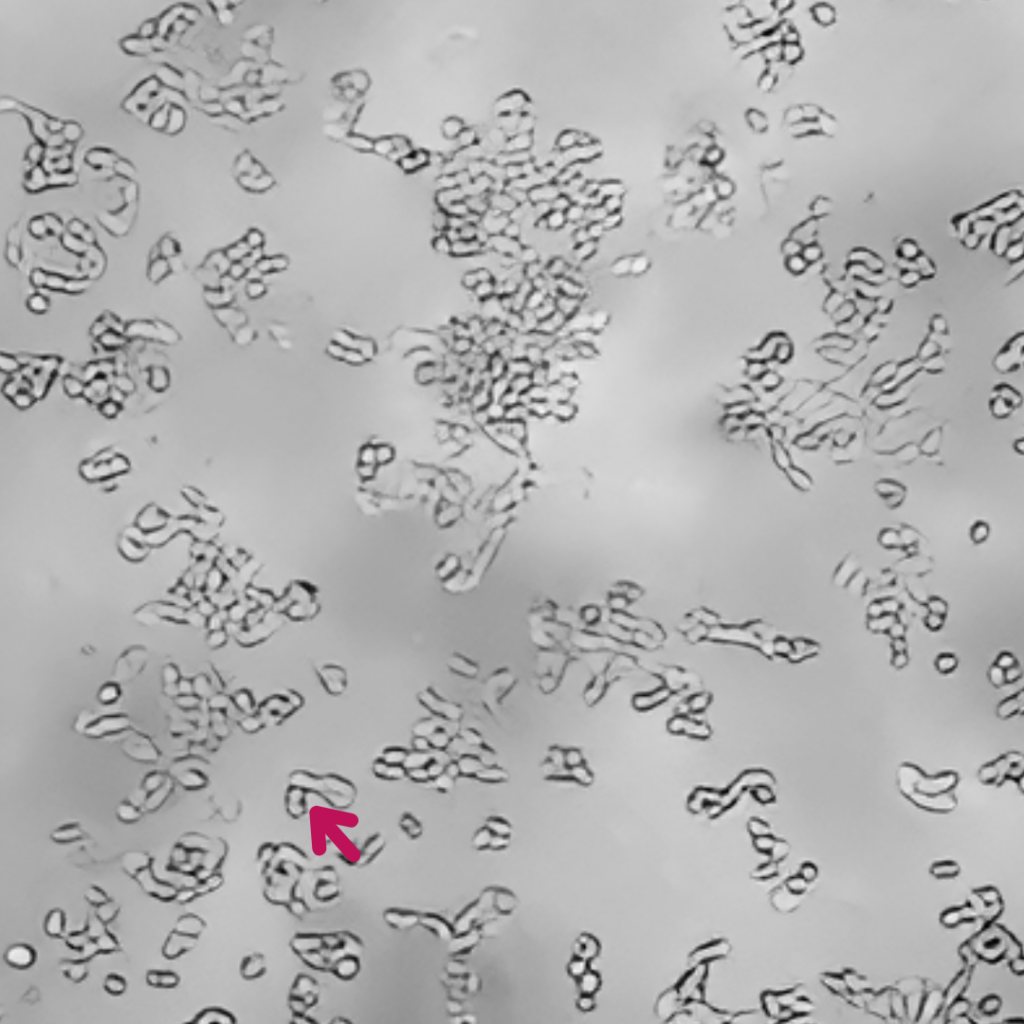
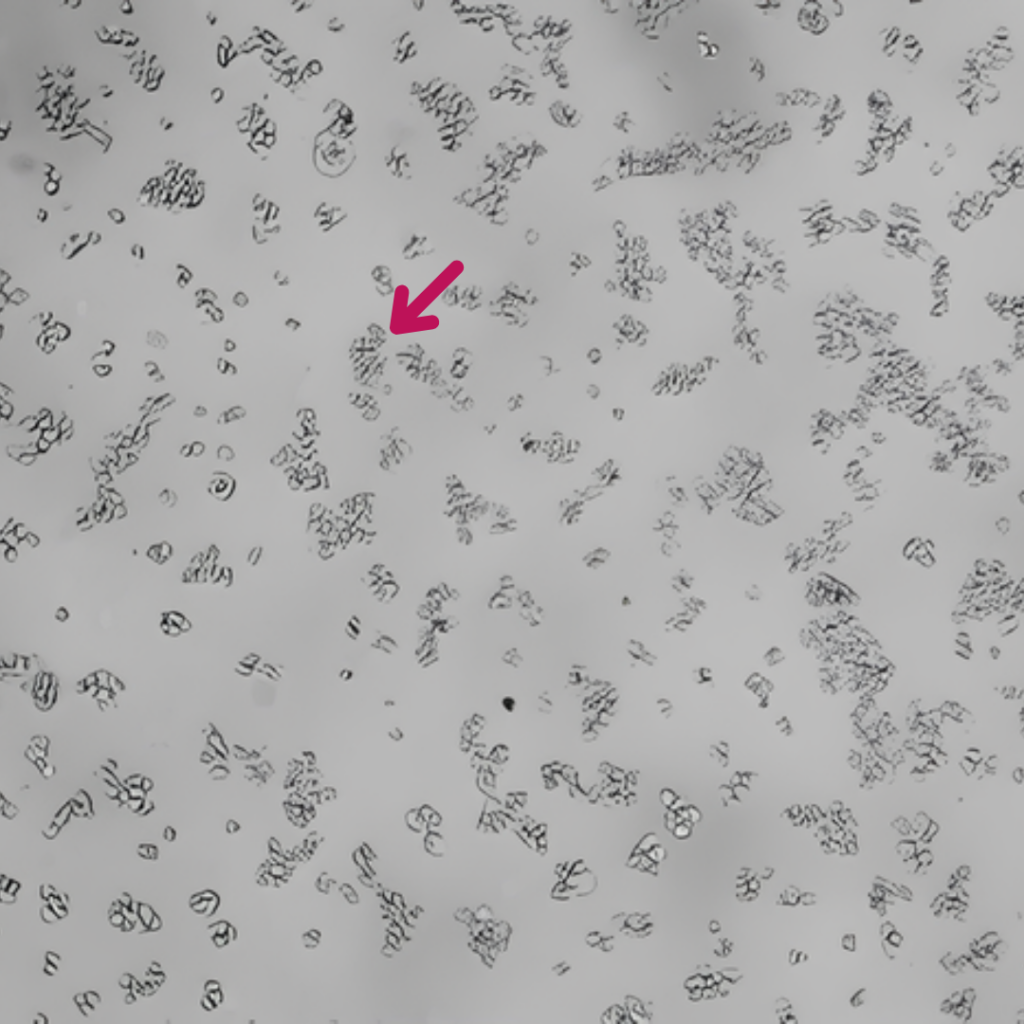
È stata dimostrata l’azione chelante di Epavin sui metalli pesanti come Cadmio, Mercurio e Piombo, nonché la sua attività antiossidante, in uno studio in vitro condotto su cellule epatiche dall’Università degli Studi di Bari Aldo Moro – Dipartimento di Farmacia e Scienze del Farmaco.
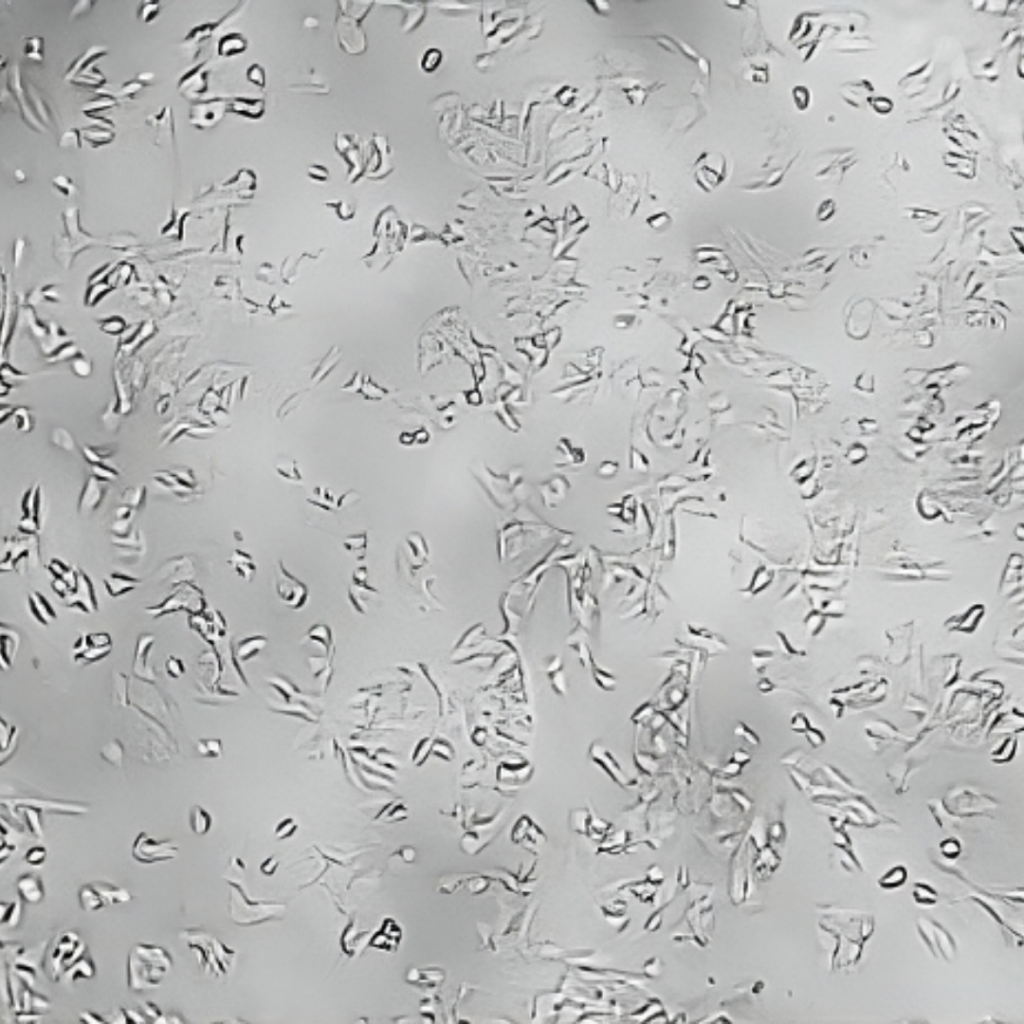
CTRL
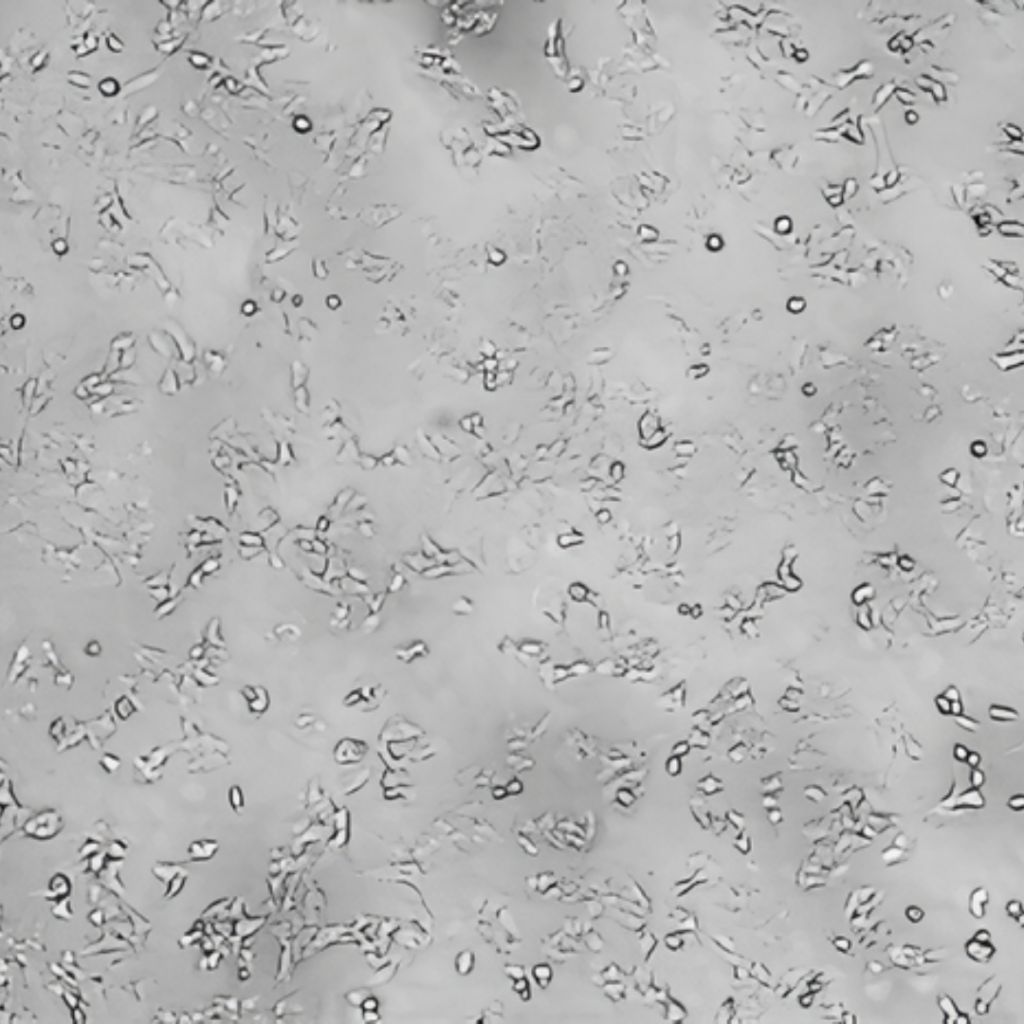
Epavin 500 μg/mL
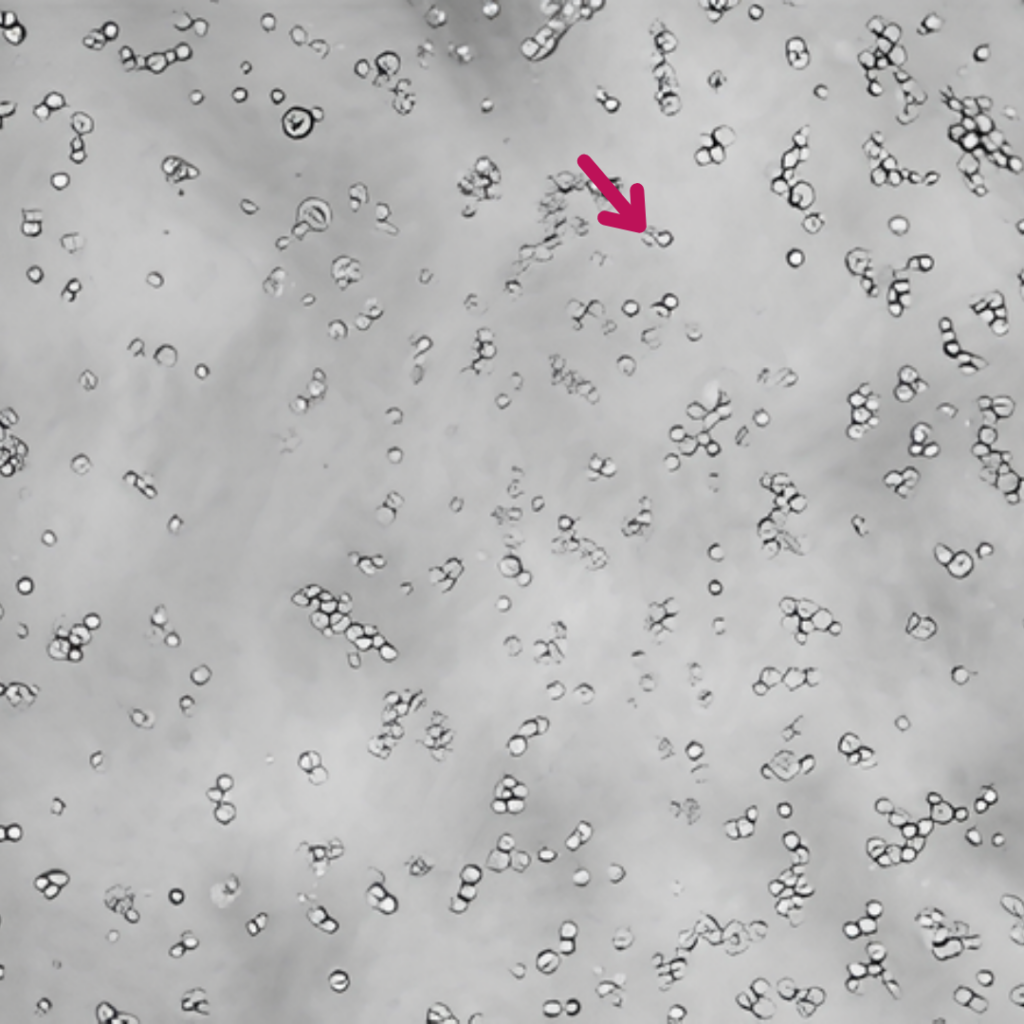
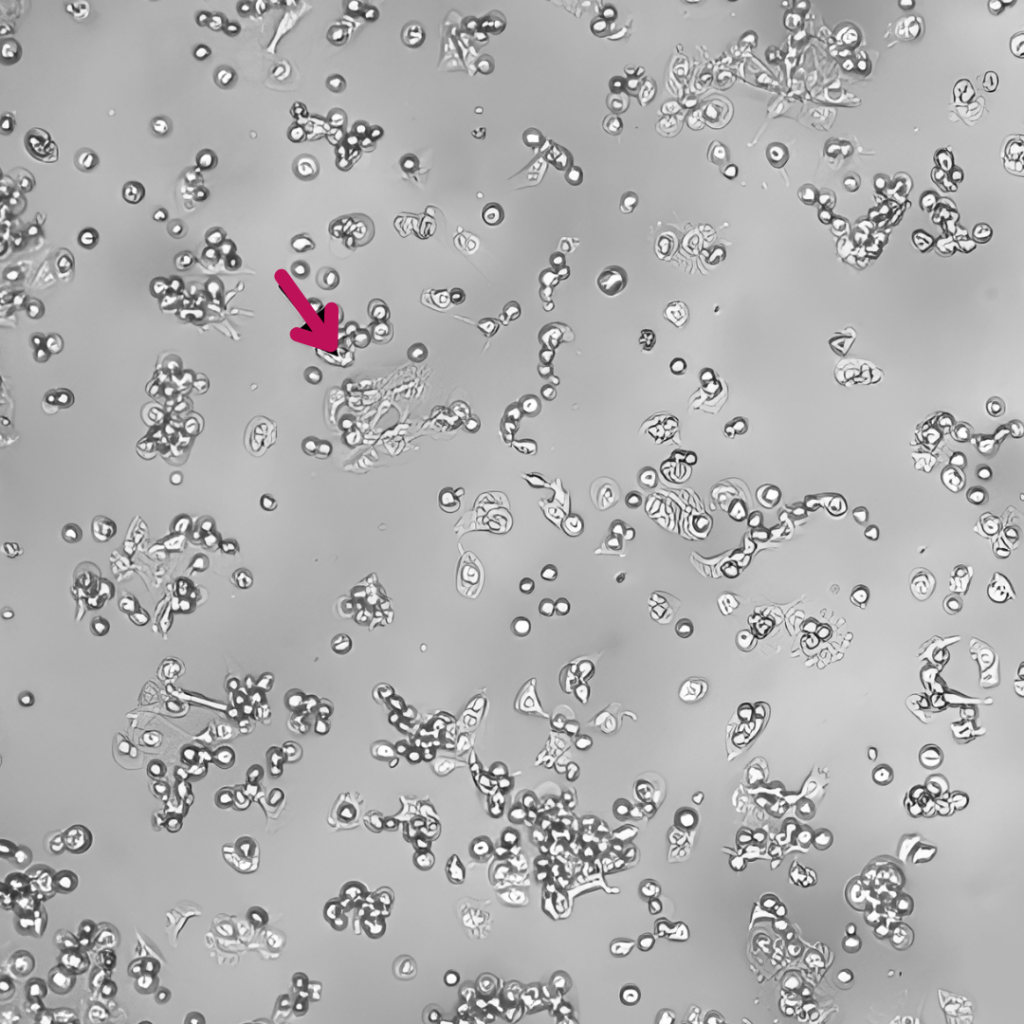
Epavin 500 μg/mL
+
Cd2+ 30 μM
Epavin 500 μg/mL
+
Hg2+ 30 μM
Pb2+ 30 μM
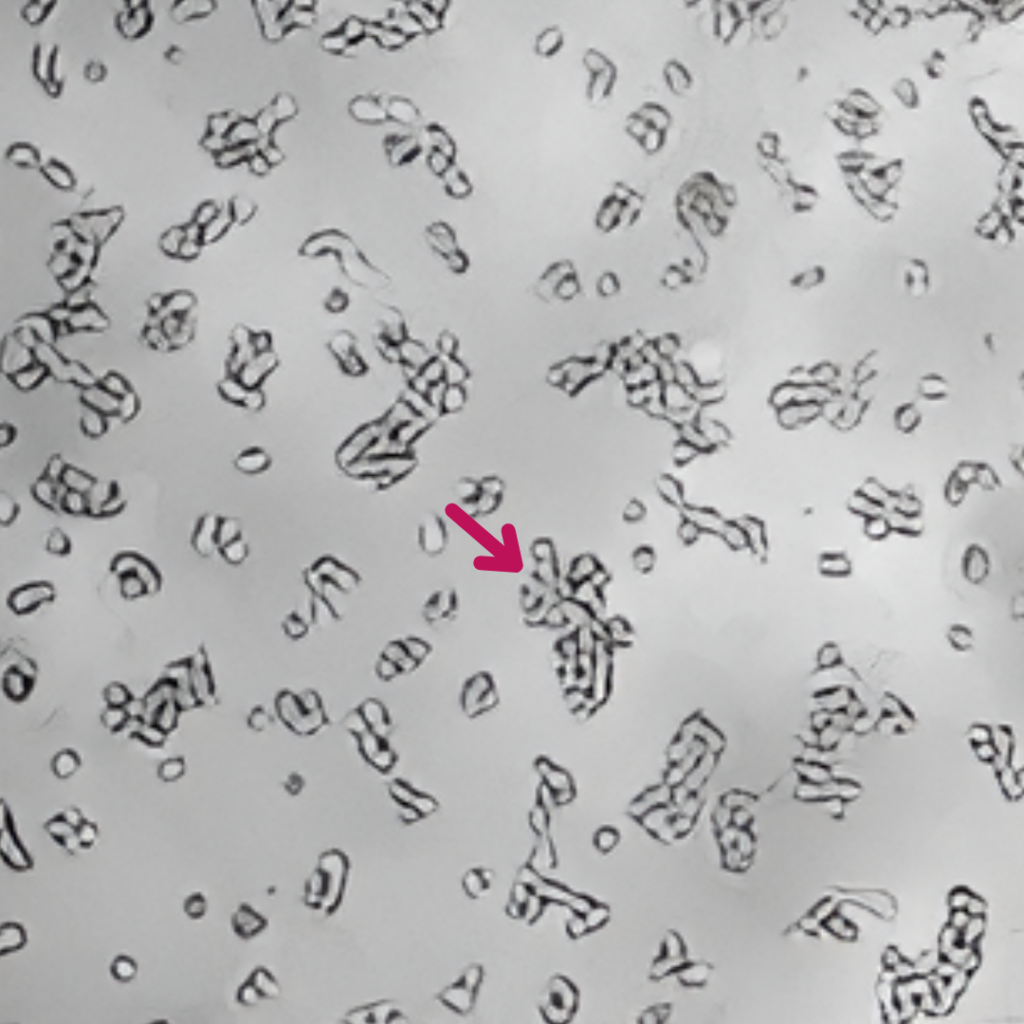
Epavin 500 μg/mL
+
Pb2+ 30 μM
I VANTAGGI DELLA
FORMULAZIONE
IN GOCCE:



MODALITÀ D’USO
30 gocce x 2 volte al dì (1 mezza pipetta = 30 gocce)
AVVERTENZE
Non usare in gravidanza e allattamento
| INFORMAZIONI NUTRIZIONALI | |
| Tenore medio degli ingredienti caratterizzanti |
Per dose max die (60 gocce = 2 ml) |
| Tarassaco radice EI | 0,25 ml |
| Cardo mariano frutto EI | 0,25 ml |
| Carciofo foglie EI | 0,25 ml |
| Crespino corteccia dei rami EI | 0,25 ml |
| Boldo foglie EI | 0,2 ml |
| Ravanello nero EI | 0,2 ml |
| Rabarbaro radice EI | 0,2 ml |
| Crisantello parti aeree EI | 0,2 ml |
| Desmodium foglie EI | 0,1 ml |
| Combreto foglie EI | 0,1 ml |
| Menta piperita | 0,02 ml |
| Rosmarino OE | 0,02 ml |
PRODOTTO
PRIVO DI ALCOL
IN DILUZIONE:
25 gocce in mezzo bicchiere di acqua come da rapporto di prova 23/000389151
BIBLIOGRAFIA: ▸
- Epidemiology and Risk Factors for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Population-Based Study (2022).
- S. R. Dincer, et al. (2013). “Effects of antioxidant therapy in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.” Hepatitis Monthly, 13(8).
- Market analysis on product carried out through a comparison of NAFLD products present in the Italian Ministry of Health database.
- Choleretic activity and biliary elimination of lipids and bile acids induced by an artichoke leaf extract in rats. Saénz Rodriguez T, García Giménez D, de la Puerta Vázquez R. Phytomedicine. 2002 Dec;9(8):687-93. doi: 10.1078/094471102321621278.
- Functional and Therapeutic Potential of Cynara scolymus in Health Benefits. Porro C, Benameur T, Cianciulli A, Vacca M, Chiarini M, De Angelis M, Panaro MA. Nutrients. 2024 Mar 17;16(6):872. doi: 10.3390/nu16060872.
- Berberine in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-A Review. Koperska A, Wesołek A, Moszak M, Szulińska M. Nutrients. 2022 Aug 23;14(17):3459. doi: 10.3390/nu14173459.
- Study in the process of publication: “Protective activity of Epavin, new comparisons of toxicity and oxidative stress induced by heavy metals” – Uniba – Department of Pharmacy, Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Sei un professionista del settore sanitario?
Compila il form per scaricare il pdf sullo studio scientifico condotto su EPAVIN
